Prenatal Genetic Testing - SNP Array
Chromosomal abnormalities cause problems
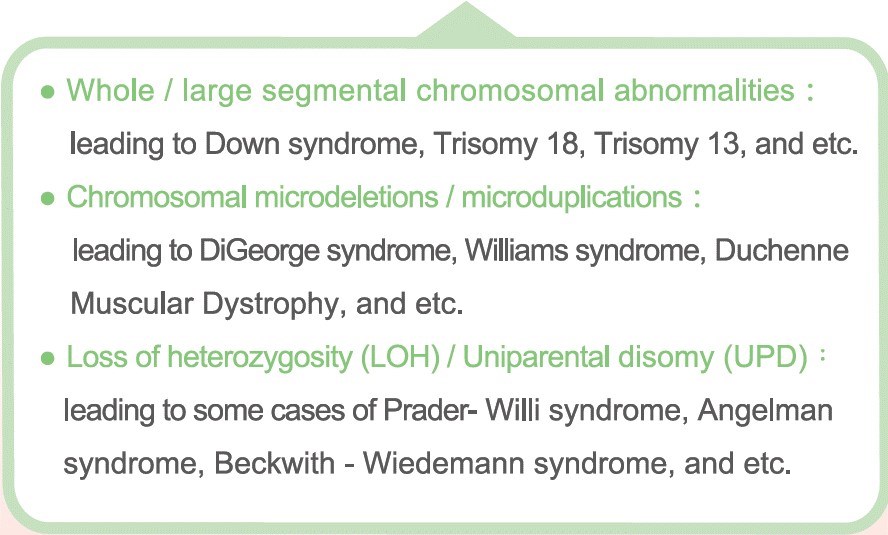
The chromosome numeral or structural variants can lead to excess or shortage of the genes within that region, resulting in a person with diseases such as Down syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, and DiGeorge syndrome.
Pregnancy at an advanced age increases the fetal risk of chromosomal abnormality.
More accurate DIAGNOSTIC testing
SNP array is a diagnostic test which is recommended for patients who have abnormal finding after a prenatal testing such as karyotyping, ultrasound or non-invasive prenatal test. Therefore, it can detect genome-wide copy number variants (CNVs) and also is recommended for patients who want to maximize the detection of fetal genetic diagnoses.
In addition, most genetic changes identified by chromosomal microarray analysis that are typically not identified on standard karyotype are not associated with increasing maternal age; therefore, the use of this test can be considered for all women, regardless of age, who undergo prenatal diagnostic testing.
When to consider testing?
- Pregnancies at high risk for chromosomal abnormalities due to abnormal prenatal findings:
- Fetal structural abnormalities detected on ultrasound scans
- Abnormal/high-risk results from non-invasive maternal serum aneuploidy screening tests(e.g. NIPT, first/second-trimester maternal serum Down syndrome screening)
- Non-invasive prenatal tests (NIPT) showing no-call or inconclusive results due to low fetal fraction
- Fetus with abnormal karyotype results requiring further clarification of risks
- Multiple gestations
- Want to maximize the detection of fetal genetic diagnoses
- Want to test for microduplications/microdeletion syndromes and lower fetal risk of chromosomal abnormalities
- Advanced maternal age
- Anyone considering invasive prenatal testing (e.g. amniocentesis) for diagnostic test results
- Family history of congenital anomalies or a previous pregnancy with a fetus with chromosomal abnormalities
- Pregnancy achieved after preimplantation genetic screening (PGS) or preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD)
Why choose GGA SNP array?
Currently, the commonly used genetic testing methods, such as karyotyping (G-banding) or array-based comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH), are limited by the comparatively lower-resolution and fewer types of genetic changes. Genetic variants such as loss of heterozygosity (LOH) or triploidy are difficult to be detect using traditional methods.
GGA SNP array with its superior sensitivity and resolution is a more EFFICIENTLY testing to detect more small variation across the whole chromosome set and provide COMPREHENSIVE genetic counseling service.
Why Choose GGA?
- COMPREHENSIVE genetic counseling
professional data analysis and counseling support to clinicians
- FASTER testing process
the result is available in a shorter time
- BETTER detection
more chromosomal abnormalities are detected, such as LOH, UPD, and triploidy
- HIGHER resolution
detection of small chromosomal variations, such as microduplication and microdeletion
Specimen Require and Notice
- Amniotic fluid:10-15mL in Sterile tube
- DNA:more than 20 μL (concentration of 50 ng/μL, 260/280 ratio greater than 1.8) into eppendorf tube and seal with parafilm
- Blood (if follow-up parental testing needed):3-5mL in Lavender top tube (EDTA)
- Turnaround time (TAT): 10 working days from receiving specimen