Expanded Carrier Screening
A simple and accurate DNA testing to check if you are a carrier for certain genetic conditions and understand if you have a higher chance to have a child with that condition.
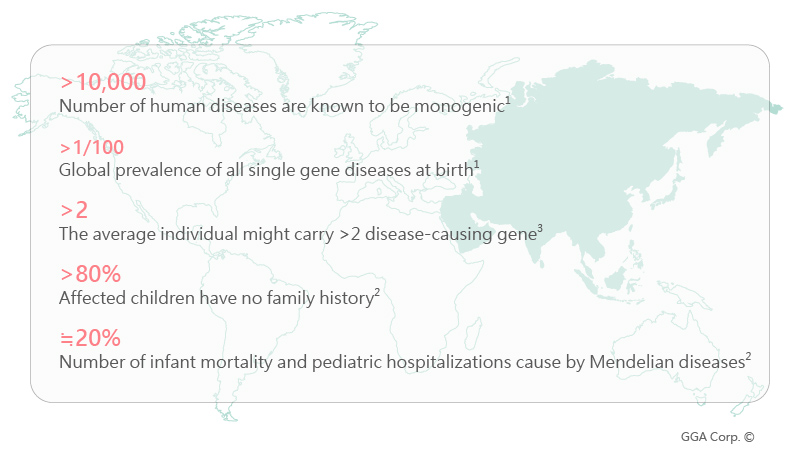
Did you know?
References:
1. http://www.who.int/genomics/public/geneticdiseases
2. PLoS Curr. 2012 May 2:e4f9877ab8ffa9
3. The American Journal of Human Genetics 91, 1022–1032, 2012.
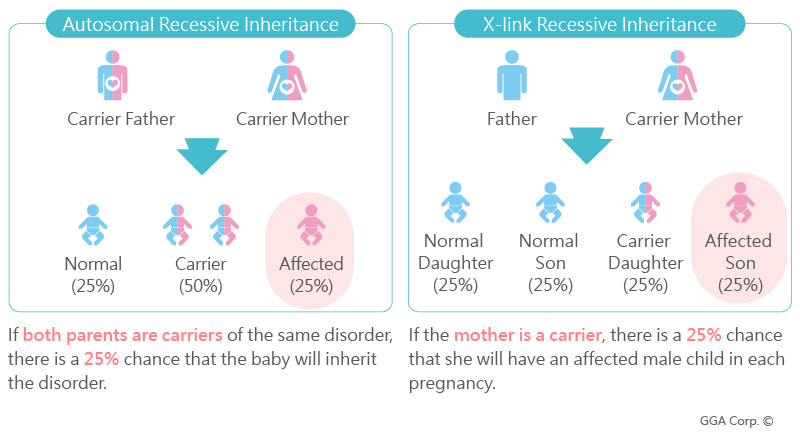
What is Genetic Carrier?
- Genetic carrier is a person that has a mutant gene of recessive disease who usually does not display or show symptoms of the disease.
- Although carriers are healthy, however, they are able to pass the genetic condition onto their offspring, who may then express the genetic trait.
- If both parents are carriers of the same disorder, there is a 25% risk that the offspring have the recessive trait in phenotype.
This test is recommended for people who:
- would like to understand their risk of having a child with a genetic disorder.
- have a family history of genetic disease
- are closely related by blood (couples)
- are pregnant or considering pregnancy
- are planning to use/ donate eggs, sperm, or embryos
Why choose GGA Expanded Carrier Screening?

GGA Expanded Carrier Screening testing options
Depending on your needs, GGA provides different testing options for you.

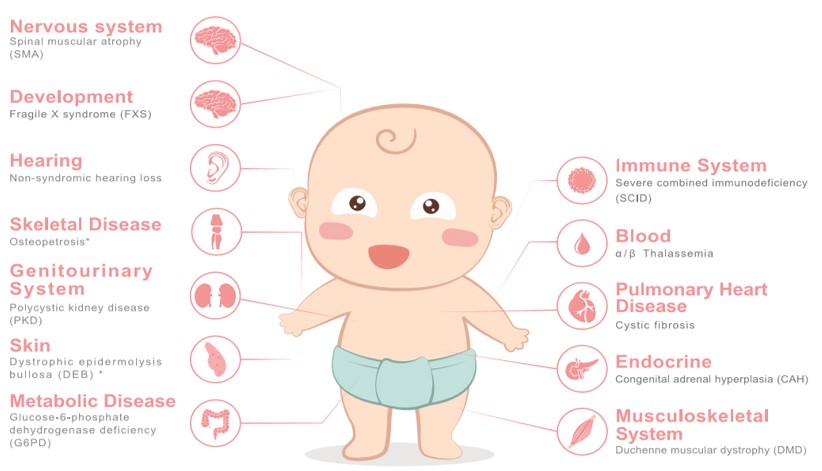
Disease categories covered:

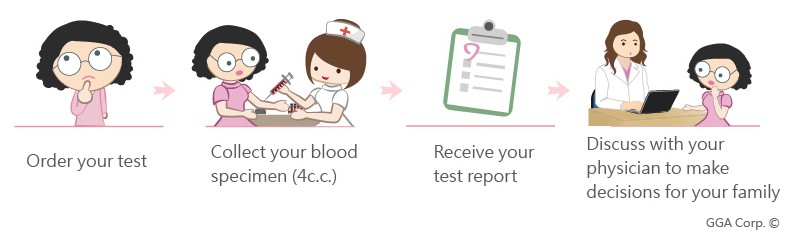
Test Process
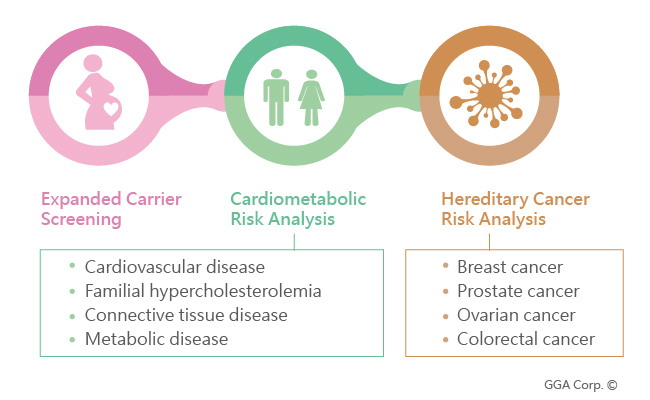
Personal Genetic Databank- Package Upgrade
GGA provides different genetic tests according to different categories. You could upgrade your testing package to discover your cardiometabolic risk and hereditary cancer risk.
Frequently asked questions
1. What should I do if my partner and I both are positive for a condition?
If you’re planning a pregnancy, you can consider In Vitro Fertilization (IVF). During the IVF process, physician will select embryos free of genetic problems through Ultra PGD/ PGT-A to implant. You can also consider other options such as implant donor’s egg or sperm that is not a carrier for the same condition.
If you’re already pregnant, you can do a diagnostic test such as amniocentesis to determine if the inherited disease was passed on to your child. Discuss with your physician for the follow up treatment.
2. Who should be tested first? Male or female?
This is flexible. However, in the cases where there is no family history of genetic disease, testing the female first is recommended due to the assessment of X-linked disorders (as male only have one X chromosome, they already be impacted if they are carrying such variants).




.jpg)
